=====================================================
redis源码学习系列文章:
redis源码分析之内存编码分析intset, ziplist编码分析
redis源码分析之对象系统源码分析string, list链表,hash哈希,set集合,zset有序集合
redis源码分析之异步进程保存数据rdb文件和aof文件源码分析
redis源码分析之集群之一的槽的分配算法crc16原理分析
=====================================================
在我的github上会持续更新Redis代码的中文分析,地址送出https://github.com/chensongpoixs/credis_source,共同学习进步
前言
在MySQL和redis配合使用时怎么保存redis中是热点数据的,比如:MySQL的中的有100万条数据redis中有10万条数据是热点数据呢,这个就需要配置redis的使用什么方式淘汰不是热点的数据
概论介绍:
LRU:即最近最久未使用算法
LRU是Least Recently Used的缩写,即最近最少使用,是一种常用的页面置换算法,选择最近最久未使用的页面予以淘汰。该算法赋予每个页面一个访问字段,用来记录一个页面自上次被访问以来所经历的时间 t,当须淘汰一个页面时,选择现有页面中其 t 值最大的,即最近最少使用的页面予以淘汰。
LFU: 即最少使用(LFU)置换算法
在采用最少使用置换算法时,应为在内存中的每个页面设置一个移位寄存器,用来记录该页面被访问的频率。该置换算法选择在之前时期使用最少的页面作为淘汰页。由于存储器具有较高的访问速度,例如100 ns,在1 ms时间内可能对某页面连续访问成千上万次,因此,通常不能直接利用计数器来记录某页被访问的次数,而是采用移位寄存器方式。每次访问某页时,便将该移位寄存器的最高位置1,再每隔一定时间(例如100 ns)右移一次。这样,在最近一段时间使用最少的页面将是∑Ri最小的页。LFU置换算法的页面访问图与LRU置换算法的访问图完全相同;或者说,利用这样一套硬件既可实现LRU算法,又可实现LFU算法。应该指出,LFU算法并不能真正反映出页面的使用情况,因为在每一时间间隔内,只是用寄存器的一位来记录页的使用情况,因此,访问一次和访问10 000次是等效的。
文章的分析流程
- 介绍redis中的八种淘汰策略
- 分析redis中的淘汰机制的原理和实现
- redis中热点数据的配置参数说明
- redis中的热点数据的执行流程图和redis中的实现分析
正文
一, 介绍redis中的八种淘汰策略机制
- volatile-lru:从已设置过期时间的数据集(server.db[i].expires)中挑选最近最久未使用的数据淘汰
- volatile-lfu: 从已设置过期时间的数据集(server.db[i].expires)中挑选最近最少使用的数据淘汰
- volatile-ttl:从已设置过期时间的数据集(server.db[i].expires)中挑选将要过期的数据淘汰
- volatile-random:从已设置过期时间的数据集(server.db[i].expires)中任意选择数据淘汰
- allkeys-lru:从数据集(server.db[i].dict)中挑选最近最久未使用的数据淘汰
- allkeys-lfu: 从数据集(server.db[i].dict)中挑选最少使用的数据淘汰
- allkeys-random:从数据集(server.db[i].dict)中任意选择数据淘汰
- no-enviction(驱逐):禁止驱逐数据
二, 分析redis中的淘汰机制的原理和实现
redis中的淘汰机制大致分为三种的分别是:
- 使用数据
- 选择任意数据淘汰
- 禁止驱逐数据
1, 使用数据 (即LRU,LFU,TTL)
- LRU的算法分析
原理分析:
创建的时候附上时间戳在查询或者更新修改之前进行热点数据的更新, 在查询或者更新的时候重新附上时间戳
在创建key-value时就赋值时间戳
robj *createObject(int type, void *ptr) {
robj *o = zmalloc(sizeof(*o));
o->type = type;
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_RAW;
o->ptr = ptr;
o->refcount = 1;
/* Set the LRU to the current lruclock (minutes resolution), or
* alternatively the LFU counter. */
if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) {
o->lru = (LFUGetTimeInMinutes()<<8) | LFU_INIT_VAL;
} else {
o->lru = LRU_CLOCK();
}
return o;
}
robj *createEmbeddedStringObject(const char *ptr, size_t len) {
robj *o = zmalloc(sizeof(robj)+sizeof(struct sdshdr8)+len+1);
struct sdshdr8 *sh = (void*)(o+1);
o->type = OBJ_STRING;
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR;
o->ptr = sh+1;
o->refcount = 1;
if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) {
o->lru = (LFUGetTimeInMinutes()<<8) | LFU_INIT_VAL;
} else {
o->lru = LRU_CLOCK(); //赋值了
}
sh->len = len;
sh->alloc = len;
sh->flags = SDS_TYPE_8;
if (ptr == SDS_NOINIT)
sh->buf[len] = '\0';
else if (ptr) {
memcpy(sh->buf,ptr,len);
sh->buf[len] = '\0';
} else {
memset(sh->buf,0,len+1);
}
return o;
}
在每次查询或者更新数据的时候在方法processCommand中都会先查看所有的数据的是否是热点数据进行更新操作之后, 在查询中的才会更新这个时间戳在方法lookupKey中
int processCommand(client *c) {
/* The QUIT command is handled separately. Normal command procs will
* go through checking for replication and QUIT will cause trouble
* when FORCE_REPLICATION is enabled and would be implemented in
* a regular command proc. */
if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[0]->ptr, "quit")) {
addReply(c, shared.ok);
c->flags |= CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY;
return C_ERR;
}
// redis search [cmd] --> [SET][GET][MSET]
/* Now lookup the command and check ASAP about trivial error conditions
* such as wrong arity, bad command name and so forth. */
c->cmd = c->lastcmd = lookupCommand(c->argv[0]->ptr);
if (!c->cmd) {
flagTransaction(c);
sds args = sdsempty();
int i;
for (i = 1; i < c->argc && sdslen(args) < 128; i++)
args = sdscatprintf(args, "`%.*s`, ", 128 - (int)sdslen(args), (char*)c->argv[i]->ptr);
addReplyErrorFormat(c, "unknown command `%s`, with args beginning with: %s",
(char*)c->argv[0]->ptr, args);
sdsfree(args);
return C_OK;
}
else if ((c->cmd->arity > 0 && c->cmd->arity != c->argc) ||
(c->argc < -c->cmd->arity)) {
flagTransaction(c);
addReplyErrorFormat(c, "wrong number of arguments for '%s' command",
c->cmd->name);
return C_OK;
}
/* Check if the user is authenticated */
if (server.requirepass && !c->authenticated && c->cmd->proc != authCommand)
{
flagTransaction(c);
addReply(c, shared.noautherr);
return C_OK;
}
/* If cluster is enabled perform the cluster redirection here.
* However we don't perform the redirection if:
* 1) The sender of this command is our master.
* 2) The command has no key arguments. */
if (server.cluster_enabled &&
!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) &&
!(c->flags & CLIENT_LUA &&
server.lua_caller->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) &&
!(c->cmd->getkeys_proc == NULL && c->cmd->firstkey == 0 &&
c->cmd->proc != execCommand))
{
int hashslot;
int error_code;
clusterNode *n = getNodeByQuery(c, c->cmd, c->argv, c->argc,
&hashslot, &error_code);
if (n == NULL || n != server.cluster->myself) {
if (c->cmd->proc == execCommand) {
discardTransaction(c);
}
else {
flagTransaction(c);
}
clusterRedirectClient(c, n, hashslot, error_code);
return C_OK;
}
}
/* Handle the maxmemory directive.
*
* First we try to free some memory if possible (if there are volatile
* keys in the dataset). If there are not the only thing we can do
* is returning an error.
*
* Note that we do not want to reclaim memory if we are here re-entering
* the event loop since there is a busy Lua script running in timeout
* condition, to avoid mixing the propagation of scripts with the propagation
* of DELs due to eviction. */
// 内存淘汰机制更新 在配置是否redis的内存的大小
if (server.maxmemory && !server.lua_timedout) {
int out_of_memory = freeMemoryIfNeeded() == C_ERR;
/* freeMemoryIfNeeded may flush slave output buffers. This may result
* into a slave, that may be the active client, to be freed. */
if (server.current_client == NULL) return C_ERR;
/* It was impossible to free enough memory, and the command the client
* is trying to execute is denied during OOM conditions? Error. */
if ((c->cmd->flags & CMD_DENYOOM) && out_of_memory) {
flagTransaction(c);
addReply(c, shared.oomerr);
return C_OK;
}
}
/* Don't accept write commands if there are problems persisting on disk
* and if this is a master instance. */
int deny_write_type = writeCommandsDeniedByDiskError();
if (deny_write_type != DISK_ERROR_TYPE_NONE &&
server.masterhost == NULL &&
(c->cmd->flags & CMD_WRITE ||
c->cmd->proc == pingCommand))
{
flagTransaction(c);
if (deny_write_type == DISK_ERROR_TYPE_RDB)
addReply(c, shared.bgsaveerr);
else
addReplySds(c,
sdscatprintf(sdsempty(),
"-MISCONF Errors writing to the AOF file: %s\r\n",
strerror(server.aof_last_write_errno)));
return C_OK;
}
/* Don't accept write commands if there are not enough good slaves and
* user configured the min-slaves-to-write option. */
if (server.masterhost == NULL &&
server.repl_min_slaves_to_write &&
server.repl_min_slaves_max_lag &&
c->cmd->flags & CMD_WRITE &&
server.repl_good_slaves_count < server.repl_min_slaves_to_write)
{
flagTransaction(c);
addReply(c, shared.noreplicaserr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Don't accept write commands if this is a read only slave. But
* accept write commands if this is our master. */
if (server.masterhost && server.repl_slave_ro &&
!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) &&
c->cmd->flags & CMD_WRITE)
{
addReply(c, shared.roslaveerr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Only allow SUBSCRIBE and UNSUBSCRIBE in the context of Pub/Sub */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_PUBSUB &&
c->cmd->proc != pingCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != subscribeCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != unsubscribeCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != psubscribeCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != punsubscribeCommand) {
addReplyError(c, "only (P)SUBSCRIBE / (P)UNSUBSCRIBE / PING / QUIT allowed in this context");
return C_OK;
}
/* Only allow commands with flag "t", such as INFO, SLAVEOF and so on,
* when slave-serve-stale-data is no and we are a slave with a broken
* link with master. */
if (server.masterhost && server.repl_state != REPL_STATE_CONNECTED &&
server.repl_serve_stale_data == 0 &&
!(c->cmd->flags & CMD_STALE))
{
flagTransaction(c);
addReply(c, shared.masterdownerr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Loading DB? Return an error if the command has not the
* CMD_LOADING flag. */
if (server.loading && !(c->cmd->flags & CMD_LOADING)) {
addReply(c, shared.loadingerr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Lua script too slow? Only allow a limited number of commands. */
if (server.lua_timedout &&
c->cmd->proc != authCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != replconfCommand &&
!(c->cmd->proc == shutdownCommand &&
c->argc == 2 &&
tolower(((char*)c->argv[1]->ptr)[0]) == 'n') &&
!(c->cmd->proc == scriptCommand &&
c->argc == 2 &&
tolower(((char*)c->argv[1]->ptr)[0]) == 'k'))
{
flagTransaction(c);
addReply(c, shared.slowscripterr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Exec the command */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI &&
c->cmd->proc != execCommand && c->cmd->proc != discardCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != multiCommand && c->cmd->proc != watchCommand)
{
queueMultiCommand(c);
addReply(c, shared.queued);
}
else {
call(c, CMD_CALL_FULL);
c->woff = server.master_repl_offset;
if (listLength(server.ready_keys))
handleClientsBlockedOnKeys();
}
return C_OK;
}
更新时间戳
/* Low level key lookup API, not actually called directly from commands
* implementations that should instead rely on lookupKeyRead(),
* lookupKeyWrite() and lookupKeyReadWithFlags(). */
robj *lookupKey(redisDb *db, robj *key, int flags) {
dictEntry *de = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr);
if (de) {
robj *val = dictGetVal(de);
/* Update the access time for the ageing algorithm.
* Don't do it if we have a saving child, as this will trigger
* a copy on write madness. */
if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 &&
server.aof_child_pid == -1 &&
!(flags & LOOKUP_NOTOUCH))
{
if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) {
updateLFU(val);
} else {
val->lru = LRU_CLOCK();
}
}
return val;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
unsigned int LRU_CLOCK(void) {
unsigned int lruclock;
// 这里我还没有完全理解下面是我的猜测 (hz的单位是 int类型--->0到1之间)
// redis是单线程IO-->所以当客户端连接数量太多时-> 可能主线程更新LRUClock的时间戳可能有误差-> 使用redis中配置动态配置这个选项
// 只有server.hz的选项小于1其大于0时就是走系统的每个都是获取当前的时间戳->是个对的系统资源消耗非常大,一般不建议使用
if (1000/server.hz <= LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION) {
atomicGet(server.lruclock,lruclock);
} else {
lruclock = getLRUClock(); // 获取秒数
}
return lruclock;
}
/* Given an object returns the min number of milliseconds the object was never
* requested, using an approximated LRU algorithm. */
unsigned long long estimateObjectIdleTime(robj *o) {
unsigned long long lruclock = LRU_CLOCK();
if (lruclock >= o->lru) {
// 记录时间戳在o->lru中的呢在每次客户端查询,更新或许插入数据时会更新这个时间戳
return (lruclock - o->lru) * LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION;
} else {
return (lruclock + (LRU_CLOCK_MAX - o->lru)) *
LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION;
}
}
}
- LFU的算法分析
原理分析:
LFU使用次数的纪录最大为255, 创建的时候附上5在查询或者更新修改之前进行热点数据的更新, 在查询或者更新的时候重新附上增加次数
- 配置选项”lfu-decay-time”是lfu以几秒减去一次
- 配置选项”lfu-log-factor”
/* Update LFU when an object is accessed.
* Firstly, decrement the counter if the decrement time is reached.
* Then logarithmically increment the counter, and update the access time. */
void updateLFU(robj *val) {
unsigned long counter = LFUDecrAndReturn(val);
counter = LFULogIncr(counter);
val->lru = (LFUGetTimeInMinutes()<<8) | counter;
}
/* Logarithmically increment a counter. The greater is the current counter value
* the less likely is that it gets really implemented. Saturate it at 255. */
uint8_t LFULogIncr(uint8_t counter) {
if (counter == 255) return 255;
double r = (double)rand()/RAND_MAX;
// 小于5
double baseval = counter - LFU_INIT_VAL;
if (baseval < 0) baseval = 0;
//感觉这个算法有点奇葩啊!!!!??? -->没有看懂哦关键
// 大于counter大5的时 r小怕时可能性比较小吧
// 当count小于5时 r小可能性也是比较小的吧
double p = 1.0/(baseval*server.lfu_log_factor+1);
if (r < p) counter++;
return counter;
}
// 返回是(255-访问次数)
unsigned long LFUDecrAndReturn(robj *o) {
unsigned long ldt = o->lru >> 8;
// lru最后8位为访问的次数
unsigned long counter = o->lru & 255;
// 秒为单位 减去次数得到num_periods
unsigned long num_periods = server.lfu_decay_time ? LFUTimeElapsed(ldt) / server.lfu_decay_time : 0;
if (num_periods)
counter = (num_periods > counter) ? 0 : counter - num_periods;
return counter;
}
- TTL
在主线程中更新这个乘于的秒数serverCron
/* Check the set of keys created by the master with an expire set in order to
* check if they should be evicted. */
void expireSlaveKeys(void) {
if (slaveKeysWithExpire == NULL ||
dictSize(slaveKeysWithExpire) == 0) return;
int cycles = 0, noexpire = 0;
mstime_t start = mstime();
while(1) {
dictEntry *de = dictGetRandomKey(slaveKeysWithExpire);
sds keyname = dictGetKey(de);
uint64_t dbids = dictGetUnsignedIntegerVal(de);
uint64_t new_dbids = 0;
/* Check the key against every database corresponding to the
* bits set in the value bitmap. */
int dbid = 0;
while(dbids && dbid < server.dbnum) {
if ((dbids & 1) != 0) {
redisDb *db = server.db+dbid;
dictEntry *expire = dictFind(db->expires,keyname);
int expired = 0;
if (expire &&
activeExpireCycleTryExpire(server.db+dbid,expire,start))
{
expired = 1;
}
/* If the key was not expired in this DB, we need to set the
* corresponding bit in the new bitmap we set as value.
* At the end of the loop if the bitmap is zero, it means we
* no longer need to keep track of this key. */
if (expire && !expired) {
noexpire++;
new_dbids |= (uint64_t)1 << dbid;
}
}
dbid++;
dbids >>= 1;
}
/* Set the new bitmap as value of the key, in the dictionary
* of keys with an expire set directly in the writable slave. Otherwise
* if the bitmap is zero, we no longer need to keep track of it. */
if (new_dbids)
dictSetUnsignedIntegerVal(de,new_dbids); // 更新 ttl的时间秒
else
dictDelete(slaveKeysWithExpire,keyname); // 删除ttl的key
/* Stop conditions: found 3 keys we cna't expire in a row or
* time limit was reached. */
cycles++;
if (noexpire > 3) break;
if ((cycles % 64) == 0 && mstime()-start > 1) break;
if (dictSize(slaveKeysWithExpire) == 0) break;
}
}
2, 选择任意数据淘汰
就内存不足情况时随机从字典中一个数据淘汰
在freeMemoryIfNeeded方法中
/* When evicting a random key, we try to evict a key for
* each DB, so we use the static 'next_db' variable to
* incrementally visit all DBs. */
for (i = 0; i < server.dbnum; i++) {
j = (++next_db) % server.dbnum;
db = server.db+j;
dict = (server.maxmemory_policy == MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_RANDOM) ?
db->dict : db->expires;
if (dictSize(dict) != 0) {
de = dictGetRandomKey(dict);
bestkey = dictGetKey(de);
bestdbid = j;
break;
}
}
函数:
随机一个数据
/* Return a random entry from the hash table. Useful to
* implement randomized algorithms */
dictEntry *dictGetRandomKey(dict *d)
{
dictEntry *he, *orighe;
unsigned long h;
int listlen, listele;
if (dictSize(d) == 0) return NULL;
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) {
do {
/* We are sure there are no elements in indexes from 0
* to rehashidx-1 */
h = d->rehashidx + (random() % (d->ht[0].size +
d->ht[1].size -
d->rehashidx));
he = (h >= d->ht[0].size) ? d->ht[1].table[h - d->ht[0].size] :
d->ht[0].table[h];
} while(he == NULL);
} else {
do {
h = random() & d->ht[0].sizemask;
he = d->ht[0].table[h];
} while(he == NULL);
}
/* Now we found a non empty bucket, but it is a linked
* list and we need to get a random element from the list.
* The only sane way to do so is counting the elements and
* select a random index. */
listlen = 0;
orighe = he;
while(he) {
he = he->next;
listlen++;
}
listele = random() % listlen;
he = orighe;
while(listele--) he = he->next;
return he;
}
三, redis中热点数据的配置参数说明
- 使用最大的内存:maxmemory
- 淘汰内存策略:maxmemory-policy
四, redis中的热点数据的执行流程图和redis中的实现分析
淘汰机制有两种情况会触发
- 客户端的查询或者插入的时会的触发,
- 客户端修改内存最大内存的配置时会触发”maxmemory”
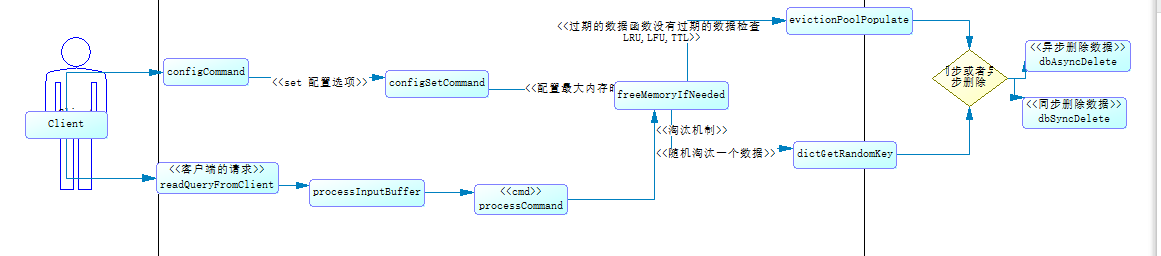
我们现在就来看看freeMemoryIfNeeded的函数的实现
int freeMemoryIfNeeded(void) {
/* By default slaves should ignore maxmemory and just be masters excat
* copies. */
// 默认不是master服务 还有是否ignore 如果忽略是等待master主从同步数据
if (server.masterhost && server.repl_slave_ignore_maxmemory) return C_OK;
size_t mem_reported, mem_tofree, mem_freed;
mstime_t latency, eviction_latency;
long long delta;
int slaves = listLength(server.slaves);
/* When clients are paused the dataset should be static not just from the
* POV of clients not being able to write, but also from the POV of
* expires and evictions of keys not being performed. */
if (clientsArePaused()) return C_OK;
if (getMaxmemoryState(&mem_reported,NULL,&mem_tofree,NULL) == C_OK)
return C_OK;
mem_freed = 0;
if (server.maxmemory_policy == MAXMEMORY_NO_EVICTION)
goto cant_free; /* We need to free memory, but policy forbids. */
latencyStartMonitor(latency);
while (mem_freed < mem_tofree) {
int j, k, i, keys_freed = 0;
static unsigned int next_db = 0;
sds bestkey = NULL;
int bestdbid;
redisDb *db;
dict *dict;
dictEntry *de;
if (server.maxmemory_policy & (MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LRU|MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) ||
server.maxmemory_policy == MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_TTL)
{
// 临时变量存在这个临时变量是内存存在所以速度很快
struct evictionPoolEntry *pool = EvictionPoolLRU;
while(bestkey == NULL) {
unsigned long total_keys = 0, keys;
/* We don't want to make local-db choices when expiring keys,
* so to start populate the eviction pool sampling keys from
* every DB. */
for (i = 0; i < server.dbnum; i++) {
db = server.db+i;
// 淘汰的机制 过期的数据函数没有过期的数据检查 ---> 这个跟过期的机制有关--1.按照访问次数计算的 2. 很少访问的数据
dict = (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_ALLKEYS) ?
db->dict : db->expires;
if ((keys = dictSize(dict)) != 0) {
evictionPoolPopulate(i, dict, db->dict, pool);
total_keys += keys;
}
}
if (!total_keys) break; /* No keys to evict. */
/* Go backward from best to worst element to evict. */
for (k = EVPOOL_SIZE-1; k >= 0; k--) {
if (pool[k].key == NULL) continue;
bestdbid = pool[k].dbid;
// 这个跟过期的机制有关
if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_ALLKEYS) {
de = dictFind(server.db[pool[k].dbid].dict,
pool[k].key);
} else {
de = dictFind(server.db[pool[k].dbid].expires,
pool[k].key);
}
/* Remove the entry from the pool. */
if (pool[k].key != pool[k].cached)
sdsfree(pool[k].key); // 内部使用申请内存
// 清空临时变量中的数据
pool[k].key = NULL;
pool[k].idle = 0;
/* If the key exists, is our pick. Otherwise it is
* a ghost and we need to try the next element. */
if (de) {
bestkey = dictGetKey(de);
break;
} else {
/* Ghost... Iterate again. */
}
}
}
}
/* volatile-random and allkeys-random policy */
else if (server.maxmemory_policy == MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_RANDOM ||
server.maxmemory_policy == MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_RANDOM)
{
/* When evicting a random key, we try to evict a key for
* each DB, so we use the static 'next_db' variable to
* incrementally visit all DBs. */
for (i = 0; i < server.dbnum; i++) {
j = (++next_db) % server.dbnum;
db = server.db+j;
dict = (server.maxmemory_policy == MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_RANDOM) ?
db->dict : db->expires;
if (dictSize(dict) != 0) {
//随机一个数据
de = dictGetRandomKey(dict);
bestkey = dictGetKey(de);
bestdbid = j;
break;
}
}
}
/* Finally remove the selected key. */
if (bestkey) {
db = server.db+bestdbid;
robj *keyobj = createStringObject(bestkey,sdslen(bestkey));
propagateExpire(db,keyobj,server.lazyfree_lazy_eviction);
/* We compute the amount of memory freed by db*Delete() alone.
* It is possible that actually the memory needed to propagate
* the DEL in AOF and replication link is greater than the one
* we are freeing removing the key, but we can't account for
* that otherwise we would never exit the loop.
*
* AOF and Output buffer memory will be freed eventually so
* we only care about memory used by the key space. */
delta = (long long) zmalloc_used_memory();
latencyStartMonitor(eviction_latency);
// 同步删除数据函数异步删除数据
if (server.lazyfree_lazy_eviction)
dbAsyncDelete(db,keyobj);
else
dbSyncDelete(db,keyobj);
latencyEndMonitor(eviction_latency);
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("eviction-del",eviction_latency);
latencyRemoveNestedEvent(latency,eviction_latency);
delta -= (long long) zmalloc_used_memory();
mem_freed += delta;
server.stat_evictedkeys++;
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EVICTED, "evicted",
keyobj, db->id);
decrRefCount(keyobj);
keys_freed++;
/* When the memory to free starts to be big enough, we may
* start spending so much time here that is impossible to
* deliver data to the slaves fast enough, so we force the
* transmission here inside the loop. */
if (slaves) flushSlavesOutputBuffers();
/* Normally our stop condition is the ability to release
* a fixed, pre-computed amount of memory. However when we
* are deleting objects in another thread, it's better to
* check, from time to time, if we already reached our target
* memory, since the "mem_freed" amount is computed only
* across the dbAsyncDelete() call, while the thread can
* release the memory all the time. */
if (server.lazyfree_lazy_eviction && !(keys_freed % 16)) {
if (getMaxmemoryState(NULL,NULL,NULL,NULL) == C_OK) {
/* Let's satisfy our stop condition. */
mem_freed = mem_tofree;
}
}
}
if (!keys_freed) {
latencyEndMonitor(latency);
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("eviction-cycle",latency);
goto cant_free; /* nothing to free... */
}
}
latencyEndMonitor(latency);
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("eviction-cycle",latency);
return C_OK;
cant_free:
/* We are here if we are not able to reclaim memory. There is only one
* last thing we can try: check if the lazyfree thread has jobs in queue
* and wait... */
while(bioPendingJobsOfType(BIO_LAZY_FREE)) {
if (((mem_reported - zmalloc_used_memory()) + mem_freed) >= mem_tofree)
break;
usleep(1000);
}
return C_ERR;
}
在evictionPoolPopulate函数中我没有明白为什么随机选择maxmemory_samples个的数据的淘汰的
void evictionPoolPopulate(int dbid, dict *sampledict, dict *keydict, struct evictionPoolEntry *pool) {
int j, k, count;
dictEntry *samples[server.maxmemory_samples];
// 这里选择还是随机选择maxmemory_samples个的数据的淘汰的----> ???
count = dictGetSomeKeys(sampledict,samples,server.maxmemory_samples);
for (j = 0; j < count; j++) {
unsigned long long idle;
sds key;
robj *o;
dictEntry *de;
de = samples[j];
key = dictGetKey(de);
/* If the dictionary we are sampling from is not the main
* dictionary (but the expires one) we need to lookup the key
* again in the key dictionary to obtain the value object. */
if (server.maxmemory_policy != MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_TTL) {
// dict与expaire
if (sampledict != keydict) de = dictFind(keydict, key);
o = dictGetVal(de);
}
/* Calculate the idle time according to the policy. This is called
* idle just because the code initially handled LRU, but is in fact
* just a score where an higher score means better candidate. */
if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LRU) {
idle = estimateObjectIdleTime(o);
} else if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) {
/* When we use an LRU policy, we sort the keys by idle time
* so that we expire keys starting from greater idle time.
* However when the policy is an LFU one, we have a frequency
* estimation, and we want to evict keys with lower frequency
* first. So inside the pool we put objects using the inverted
* frequency subtracting the actual frequency to the maximum
* frequency of 255. */
idle = 255-LFUDecrAndReturn(o);
} else if (server.maxmemory_policy == MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_TTL) {
/* In this case the sooner the expire the better. */
idle = ULLONG_MAX - (long)dictGetVal(de);
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown eviction policy in evictionPoolPopulate()");
}
/* Insert the element inside the pool.
* First, find the first empty bucket or the first populated
* bucket that has an idle time smaller than our idle time. */
k = 0;
// 这里就关键淘汰的算法 选择idle的ttl可能大的淘汰 ---> 是有条件哦 idle关键变量[idle]
while (k < EVPOOL_SIZE &&
pool[k].key &&
pool[k].idle < idle) k++;
if (k == 0 && pool[EVPOOL_SIZE-1].key != NULL) {
/* Can't insert if the element is < the worst element we have
* and there are no empty buckets. */
continue;
} else if (k < EVPOOL_SIZE && pool[k].key == NULL) {
// 1.正常情况都会走这边, 在下面有插入的流程
/* Inserting into empty position. No setup needed before insert. */
} else {
// 以后会走这边的流程
/* Inserting in the middle. Now k points to the first element
* greater than the element to insert. */
if (pool[EVPOOL_SIZE-1].key == NULL) {
// 移动数组腾出位置出来
/* Free space on the right? Insert at k shifting
* all the elements from k to end to the right. */
/* Save SDS before overwriting. */
sds cached = pool[EVPOOL_SIZE-1].cached;
memmove(pool+k+1, pool+k, sizeof(pool[0])*(EVPOOL_SIZE-k-1));
pool[k].cached = cached;
} else {
/* No free space on right? Insert at k-1 */
k--;
/* Shift all elements on the left of k (included) to the
* left, so we discard the element with smaller idle time. */
sds cached = pool[0].cached; /* Save SDS before overwriting. */
// 这个只是 key的长度大于255个字节的就申请的动态内存保持数据了的所以不要的时候的释放内存
if (pool[0].key != pool[0].cached) sdsfree(pool[0].key);
memmove(pool, pool+1, sizeof(pool[0])*k);
pool[k].cached = cached;
}
}
/* Try to reuse the cached SDS string allocated in the pool entry,
* because allocating and deallocating this object is costly
* (according to the profiler, not my fantasy. Remember:
* premature optimizbla bla bla bla. */
int klen = sdslen(key);
if (klen > EVPOOL_CACHED_SDS_SIZE) {
pool[k].key = sdsdup(key);
} else {
memcpy(pool[k].cached,key,klen+1);
sdssetlen(pool[k].cached,klen);
pool[k].key = pool[k].cached;
}
pool[k].idle = idle;
pool[k].dbid = dbid;
}
}
这个是随便在找数据吗?
unsigned int dictGetSomeKeys(dict *d, dictEntry **des, unsigned int count) {
unsigned long j; /* internal hash table id, 0 or 1. */
unsigned long tables; /* 1 or 2 tables? */
unsigned long stored = 0, maxsizemask;
unsigned long maxsteps;
if (dictSize(d) < count) count = dictSize(d);
maxsteps = count*10;
/* Try to do a rehashing work proportional to 'count'. */
for (j = 0; j < count; j++) {
if (dictIsRehashing(d))
_dictRehashStep(d);
else
break;
}
tables = dictIsRehashing(d) ? 2 : 1;
maxsizemask = d->ht[0].sizemask;
if (tables > 1 && maxsizemask < d->ht[1].sizemask)
maxsizemask = d->ht[1].sizemask;
/* Pick a random point inside the larger table. */
unsigned long i = random() & maxsizemask;
unsigned long emptylen = 0; /* Continuous empty entries so far. */
while(stored < count && maxsteps--) {
for (j = 0; j < tables; j++) {
/* Invariant of the dict.c rehashing: up to the indexes already
* visited in ht[0] during the rehashing, there are no populated
* buckets, so we can skip ht[0] for indexes between 0 and idx-1. */
if (tables == 2 && j == 0 && i < (unsigned long) d->rehashidx) {
/* Moreover, if we are currently out of range in the second
* table, there will be no elements in both tables up to
* the current rehashing index, so we jump if possible.
* (this happens when going from big to small table). */
if (i >= d->ht[1].size)
i = d->rehashidx;
else
continue;
}
if (i >= d->ht[j].size) continue; /* Out of range for this table. */
dictEntry *he = d->ht[j].table[i];
/* Count contiguous empty buckets, and jump to other
* locations if they reach 'count' (with a minimum of 5). */
if (he == NULL) {
emptylen++;
if (emptylen >= 5 && emptylen > count) {
i = random() & maxsizemask;
emptylen = 0;
}
} else {
emptylen = 0;
while (he) {
/* Collect all the elements of the buckets found non
* empty while iterating. */
*des = he;
des++;
he = he->next;
stored++;
if (stored == count) return stored;
}
}
}
i = (i+1) & maxsizemask;
}
return stored;
}