=====================================================
redis源码学习系列文章:
redis源码分析之内存编码分析intset, ziplist编码分析
redis源码分析之对象系统源码分析string, list链表,hash哈希,set集合,zset有序集合
redis源码分析之异步进程保存数据rdb文件和aof文件源码分析
=====================================================
在我的github上会持续更新Redis代码的中文分析,地址送出https://github.com/chensongpoixs/credis_source,共同学习进步
前言
学习redis源码中布隆过滤器时, 发现redis中建立伯努利数学模型来统计pfcount的次数
正文
一, redis中布隆过滤器代码分析
布隆过滤器一个是插入”一条数据” 和查询有多少条“数据”
需要了解redis中布隆过滤器是基于概率的, 数据统计的计算出来的。 里面有桶的概念
1, 插入”一条数据”
插入数据的流程图

对应的hllPatLen函数的代码分析
/* Given a string element to add to the HyperLogLog, returns the length
* of the pattern 000..1 of the element hash. As a side effect 'regp' is
* set to the register index this element hashes to. */
int hllPatLen(unsigned char *ele, size_t elesize, long *regp) {
uint64_t hash, bit, index;
int count;
/* Count the number of zeroes starting from bit HLL_REGISTERS
* (that is a power of two corresponding to the first bit we don't use
* as index). The max run can be 64-P+1 = Q+1 bits.
*
* Note that the final "1" ending the sequence of zeroes must be
* included in the count, so if we find "001" the count is 3, and
* the smallest count possible is no zeroes at all, just a 1 bit
* at the first position, that is a count of 1.
*
* This may sound like inefficient, but actually in the average case
* there are high probabilities to find a 1 after a few iterations. */
hash = MurmurHash64A(ele,elesize,0xadc83b19ULL);
// 低的14位作为下标索引
index = hash & HLL_P_MASK/*0011 1111 1111 1111*/; /* Register index. */
//取高的50位数据作为count数据的操作
//00 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
hash >>= HLL_P; /* 高于14位 数据保留下来 Remove bits used to address the register. */
// 把第50位改为1 决定count的最大值是 50
//10 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
hash |= ((uint64_t)1<<HLL_Q); /* Make sure the loop terminates
and count will be <= Q+1. */
bit = 1; // 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001
count = 1; /* Initialized to 1 since we count the "00000...1" pattern. */
while((hash & bit) == 0) {
count++; //为什么要这样制定count的值
bit <<= 1;
}
*regp = (int) index;
return count;
}
- hllDenseSet方法分析
这个需要知道 count实际储存到内存中只有6个字节的
/* Note: if we access the last counter, we will also access the b+1 byte
* that is out of the array, but sds strings always have an implicit null
* term, so the byte exists, and we can skip the conditional (or the need
* to allocate 1 byte more explicitly). */
/* Store the value of the register at position 'regnum' into variable 'target'.
* 'p' is an array of unsigned bytes. */
// 它里面操作的目的是 保存 1-52的数字到6个bit位中去 这个是这个函数要达到的目的 所以怎么实现也就无所谓了
#define HLL_DENSE_GET_REGISTER(target,p,regnum) do { \
uint8_t *_p = (uint8_t*) p; \
unsigned long _byte = regnum*HLL_BITS/8;/* 8 = 2 ^ 3 ==> 操作数 >> 3*/ \
unsigned long _fb = regnum*HLL_BITS&7; \
unsigned long _fb8 = 8 - _fb; \
unsigned long b0 = _p[_byte]; \
unsigned long b1 = _p[_byte+1]; \
target = ((b0 >> _fb) | (b1 << _fb8)) & HLL_REGISTER_MAX; /* HLL_REGISTER_MAX ==> 0011 1111*/ \
} while(0)
/* Set the value of the register at position 'regnum' to 'val'.
* 'p' is an array of unsigned bytes. */
#define HLL_DENSE_SET_REGISTER(p,regnum,val) do { \
uint8_t *_p = (uint8_t*) p; \
unsigned long _byte = regnum*HLL_BITS/8;/*在初始化时 内存大小计算公式 = (HLL_REGISTERS*HLL_BITS+7)/8) */ \
unsigned long _fb = regnum*HLL_BITS&7; /* 只有regnum的个位上是2和7可以 _fd != 0的操作*/ \
unsigned long _fb8 = 8 - _fb; \
unsigned long _v = val; \
_p[_byte] &= ~(HLL_REGISTER_MAX << _fb); \
_p[_byte] |= _v << _fb; /*0011 0100 => [<< 2] => 1101 0000 */ \
_p[_byte+1] &= ~(HLL_REGISTER_MAX >> _fb8); \
_p[_byte+1] |= _v >> _fb8; /*0011 0100 => [>> 6] => 0000 0011*/\
} while(0)
int hllDenseSet(uint8_t *registers, long index, uint8_t count) {
uint8_t oldcount;
HLL_DENSE_GET_REGISTER(oldcount,registers,index);
if (count > oldcount) {
HLL_DENSE_SET_REGISTER(registers,index,count);
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
2,查询有多少条数据
查询的流程图

- 52个桶数据获取 代码分析
/* Compute the register histogram in the dense representation. */
void hllDenseRegHisto(uint8_t *registers/*实际内存数据*/, int* reghisto/*桶*/) {
int j;
/* Redis default is to use 16384 registers 6 bits each. The code works
* with other values by modifying the defines, but for our target value
* we take a faster path with unrolled loops. */
if (HLL_REGISTERS == 16384 && HLL_BITS == 6) {
/*char * ptr = s_malloc(86016>>2);
if (ptr)
{
byte2hex(ptr, (const unsigned char *)registers, 86016>>2);
printf("[%s][%d][hex=%s]\n", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__, __LINE__, ptr);
s_free(ptr);
}*/
uint8_t *r = registers;
unsigned long r0, r1, r2, r3, r4, r5, r6, r7, r8, r9,
r10, r11, r12, r13, r14, r15;
// 一共内存的大小是 86016 ---> 下面统计时使用的内存大小是 12288--->还有没有使用的内存??怎么处理呢
for (j = 0; j < 1024; j++) {
/* Handle 16 registers per iteration. */
r0 = r[0] & 63; // 63 => 0011 1111
r1 = (r[0] >> 6 | r[1] << 2) & 63;
r2 = (r[1] >> 4 | r[2] << 4) & 63;
r3 = (r[2] >> 2) & 63;
r4 = r[3] & 63;
r5 = (r[3] >> 6 | r[4] << 2) & 63;
r6 = (r[4] >> 4 | r[5] << 4) & 63;
r7 = (r[5] >> 2) & 63;
r8 = r[6] & 63;
r9 = (r[6] >> 6 | r[7] << 2) & 63;
r10 = (r[7] >> 4 | r[8] << 4) & 63;
r11 = (r[8] >> 2) & 63;
r12 = r[9] & 63;
r13 = (r[9] >> 6 | r[10] << 2) & 63;
r14 = (r[10] >> 4 | r[11] << 4) & 63;
r15 = (r[11] >> 2) & 63;
// 还记得在生成hash值时产生的count值的范围吗? [1 <= count <= 51] ?? 思考一下
reghisto[r0]++;
reghisto[r1]++;
reghisto[r2]++;
reghisto[r3]++;
reghisto[r4]++;
reghisto[r5]++;
reghisto[r6]++;
reghisto[r7]++;
reghisto[r8]++;
reghisto[r9]++;
reghisto[r10]++;
reghisto[r11]++;
reghisto[r12]++;
reghisto[r13]++;
reghisto[r14]++;
reghisto[r15]++;
// 指针数组增加移动
r += 12;
}
} else {
for(j = 0; j < HLL_REGISTERS; j++) {
unsigned long reg;
HLL_DENSE_GET_REGISTER(reg,registers,j);
reghisto[reg]++;
}
}
}
- 基于类似于伯努利试验的代码分析
/* Return the approximated cardinality of the set based on the harmonic
* mean of the registers values. 'hdr' points to the start of the SDS
* representing the String object holding the HLL representation.
*
* If the sparse representation of the HLL object is not valid, the integer
* pointed by 'invalid' is set to non-zero, otherwise it is left untouched.
*
* hllCount() supports a special internal-only encoding of HLL_RAW, that
* is, hdr->registers will point to an uint8_t array of HLL_REGISTERS element.
* This is useful in order to speedup PFCOUNT when called against multiple
* keys (no need to work with 6-bit integers encoding). */
uint64_t hllCount(struct hllhdr *hdr, int *invalid) {
double m = HLL_REGISTERS;
double E;
int j;
int reghisto[HLL_Q+2] = {0}; // 52
/* Compute register histogram */
if (hdr->encoding == HLL_DENSE) {
hllDenseRegHisto(hdr->registers,reghisto);
} else if (hdr->encoding == HLL_SPARSE) {
hllSparseRegHisto(hdr->registers, sdslen((sds)hdr)-HLL_HDR_SIZE,invalid,reghisto);
} else if (hdr->encoding == HLL_RAW) {
hllRawRegHisto(hdr->registers,reghisto);
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown HyperLogLog encoding in hllCount()");
}
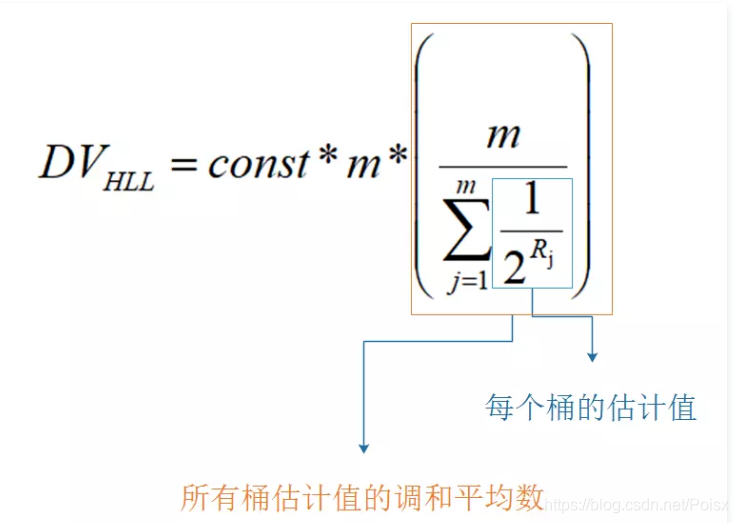
/* Estimate cardinality form register histogram. See:
* "New cardinality estimation algorithms for HyperLogLog sketches"
* Otmar Ertl, arXiv:1702.01284 */
// m *((16384 - [52]) /m)
//1. 调和平均数
// 调和平均数 公式 = n((1/a1 + 1/a2 + ... + 1/an)/2)
double z = m * hllTau((m-reghisto[HLL_Q+1])/(double)m);
//仔细观察 没有把第一个数据reghisto[0]和最后一个数据reghisto[51] 加入进入 ---> 正态分布
for (j = HLL_Q; j >= 1; --j) {
z += reghisto[j];
z *= 0.5;
}
//2. 标准误差 计算
z += m * hllSigma(reghisto[0]/(double)m);
// 调和平均数使用 0.5/ln(2)
// 公式的应用 基数统计
E = llroundl(HLL_ALPHA_INF*m*m/z);
return (uint64_t) E;
}
二, 布隆过滤器的数学原理分析
伯努利模型的原理
- 事件的各自独立的事件
- 结果只有两个可能(类似于抛硬币的只有正反面两种可能)
公式 $P_n(k) = C^k_np^k(1-p)^{n-k} = C^k_np^kq^{n-k} [q = 1-p]$
基于上面的抛硬币的试验
我们抛硬币只记录 抛硬币出现正面的时的 抛硬币的次数记为A 当我们继续大量试验 , 看可以得到一个比较均匀的A的值,
这个就和我们布隆过滤器的原理是差不多的, 布隆过滤器中使用 桶为 我们的次数A,中可能就6个字节的