前言
任务队列的的调度的使用
正文
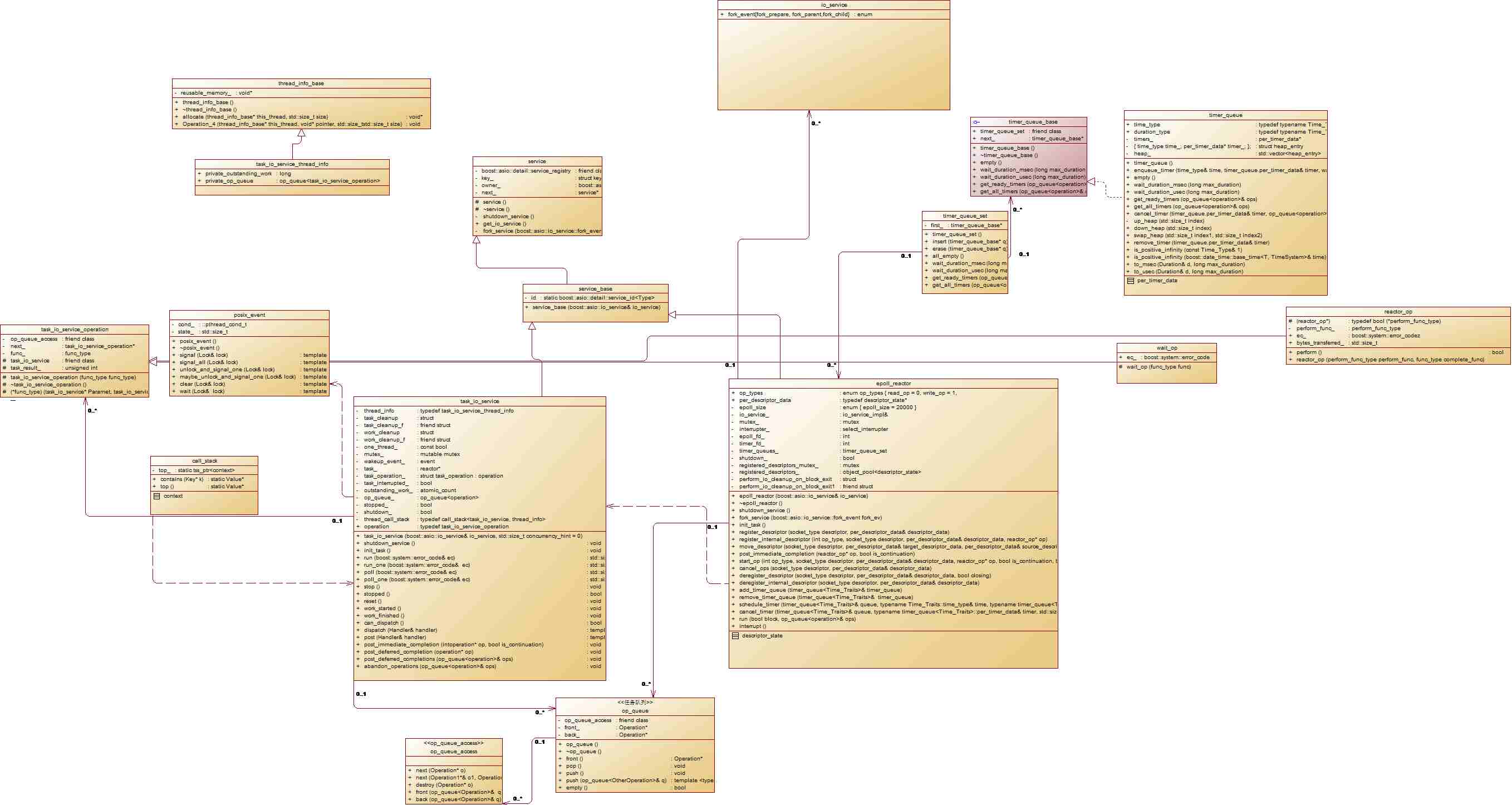
一, boost库asio io_service 的介绍
io_servie是接口类,为实现跨平台,采用了策略模式,所有接口均有impl_type实现。根据平台不同impl_type分为
win_iocp_io_service Win版本的实现,这里主要分析Linux版本。
task_io_service 非win平台下的实现,其代码结构为:
detail/task_io_service_fwd.hpp 简单声明task_io_service名称
detail/task_io_service.hpp 声明task_io_service的方法和属性
detail/impl/task_io_service.ipp 具体实现文件
队列中的任务类型为opertioan,原型其实是typedef task_io_service_operation operation,其实现文件在detail/task_io_service_operation.hpp中,当队列中的任务被执行时,就是task_io_service_operation:complete被调用的时候。
下面是task_io_service类的图
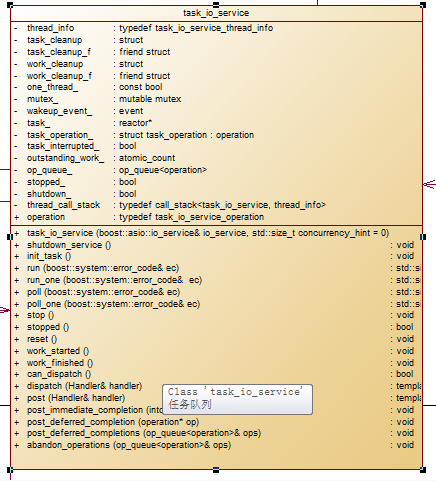
二, task_io_service::run方法
实际调用do_run_one函数
1, 优先处理队列中的任务
回调task_io_service_operation::complete函数处理 队列任务
任务队列在上面一篇文章已经介绍过来 是 使用设计模式中 模板方法模式
类的关系图

2, 没有任务时
没有任务实际时阻塞 _task->run方法中 task_变量类型为reactor,在linux平台实现为epoll_reactor,实现代码文件为detail/impl/epoll_reactor.ipp,run方法实际上执行的是epoll_wait,run阻塞在epoll_wait上等待事件到来,并且处理完事件后将需要回调的函数push到io_servie的任务队列中,虽然epoll_wait是阻塞的,但是它提供了interrupt函数,该interrupt是如何实现的呢,它向epoll_wait添加一个文件描述符,该文件描述符中有8个字节可读,这个文件描述符是专用于中断epoll_wait的,他被封装到select_interrupter中,select_interrupter实际上实现是eventfd_select_interrupter,在构造的时候通过pipe系统调用创建两个文件描述符,然后预先通过write_fd写8个字节,这8个字节一直保留。在添加到epoll_wait中采用EPOLLET水平触发,这样,只要select_interrupter的读文件描述符添加到epoll_wait中,立即中断epoll_wait。很是巧妙。
3, Run方法的原则是
- 有任务立即执行任务,尽量使所有的线程一起执行任务
- 若没有任务,阻塞在epoll_wait上等待io事件
- 若有新任务到来,并且没有空闲线程,那么先中断epoll_wait,先执行任务
- 若队列中有任务,并且也需要epoll_wait监听事件,那么非阻塞调用epoll_wait(timeout字段设置为0),待任务执行完毕在阻塞在epoll_wait上。
- 几乎对线程的使用上达到了极致。
- 从这个函数中可以知道,在使用ASIO时,io_servie应该尽量多,这样可以使其epoll_wait占用的时间片最多,这样可以最大限度的响应IO事件,降低响应时延。但是每个task_io_servie::run占用一个线程,所以task_io_servie最佳应该和CPU的核数相同。

Linux下查看某个进程的线程数量
top -Hp 进程号
三, boost中计时器
简单使用案例:
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/asio.hpp>
#include <boost/thread.hpp>
#include <boost/date_time/posix_time/posix_time.hpp>
void time_callback(const boost::system::error_code &ec,
boost::asio::deadline_timer* pt,
int * pcount)
{
//if (*pcount < 3)
{
std::cout << "count = " << *pcount << std::endl;
std::cout << boost::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
(*pcount)++;
pt->expires_at(pt->expires_at() + boost::posix_time::seconds(5));
pt->async_wait(boost::bind(time_callback, boost::asio::placeholders::error, pt, pcount));
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::cout << boost::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
boost::asio::io_service io;
boost::asio::deadline_timer t(io, boost::posix_time::seconds(5));
int count = 0;
t.async_wait(boost::bind(time_callback, boost::asio::placeholders::error, &t, &count));
std::cout << "to run" << std::endl;
io.run();
std::cout << "Final count is " << count << "\n";
std::cout << "exit" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
basic_deadline_timer 模板继承于 deadline_timer_service模板
template <typename Time,
typename TimeTraits = boost::asio::time_traits<Time>,
typename TimerService = deadline_timer_service<Time, TimeTraits> >
class basic_deadline_timer
: public basic_io_object<TimerService>
basic_deadline_timer 模板继承于 deadline_timer_service模板
template <typename Time,
typename TimeTraits = boost::asio::time_traits<Time>,
typename TimerService = deadline_timer_service<Time, TimeTraits> >
class basic_deadline_timer
: public basic_io_object<TimerService>
deadline_timer_service.hpp 服务管理scheduler_就是epoll_reactor
在timer_scheduler_fwd.hpp区别平台
#if defined(BOOST_ASIO_WINDOWS_RUNTIME)
typedef class winrt_timer_scheduler timer_scheduler;
#elif defined(BOOST_ASIO_HAS_IOCP)
typedef class win_iocp_io_service timer_scheduler;
#elif defined(BOOST_ASIO_HAS_EPOLL)
typedef class epoll_reactor timer_scheduler;
#elif defined(BOOST_ASIO_HAS_KQUEUE)
typedef class kqueue_reactor timer_scheduler;
#elif defined(BOOST_ASIO_HAS_DEV_POLL)
typedef class dev_poll_reactor timer_scheduler;
#else
typedef class select_reactor timer_scheduler;
#endif
在构造函数中 添加epoll监听
// Constructor.
deadline_timer_service(boost::asio::io_service& io_service)
: scheduler_(boost::asio::use_service<timer_scheduler>(io_service))
{
scheduler_.init_task();
scheduler_.add_timer_queue(timer_queue_); // add timer queue
}
在async_wait中添加回调函数
// Start an asynchronous wait on the timer.
template <typename Handler>
void async_wait(implementation_type& impl, Handler& handler)
{
// Allocate and construct an operation to wrap the handler.
typedef wait_handler<Handler> op;
typename op::ptr p = { boost::asio::detail::addressof(handler),
boost_asio_handler_alloc_helpers::allocate(
sizeof(op), handler), 0 };
p.p = new (p.v) op(handler);
impl.might_have_pending_waits = true;
BOOST_ASIO_HANDLER_CREATION((p.p, "deadline_timer", &impl, "async_wait"));
scheduler_.schedule_timer(timer_queue_, impl.expiry, impl.timer_data, p.p);// add epoll
p.v = p.p = 0;
}
使用boost库中计时器需要注意的要使用新的io_service服务 和io的分开