前言
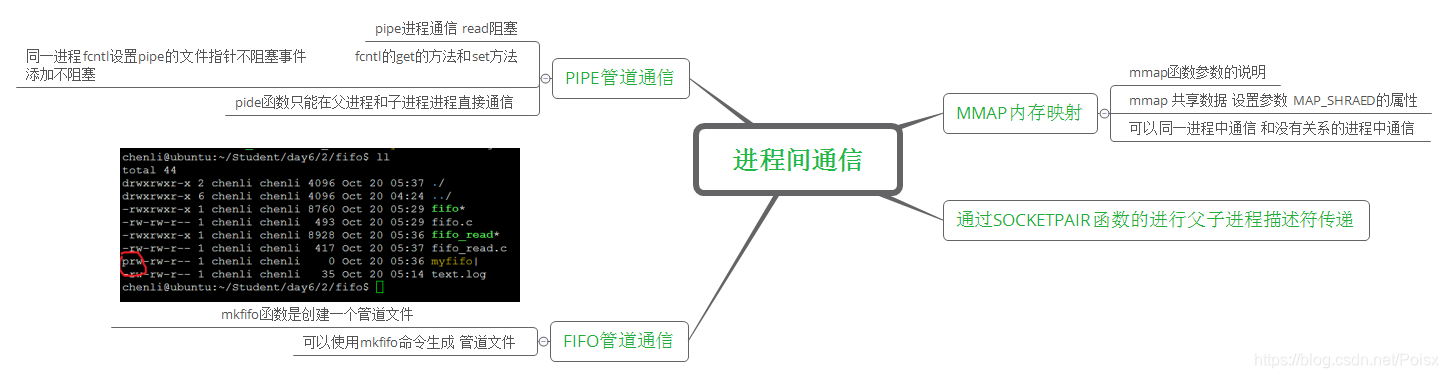
父子进程之间的通信的有五种
- 管道进程的pipe函数和dup2函数组合使用父子进程间通信
- 管道 mkfifio函数的使用
- mmap内存映射的机制
- socketpair函数的父子进程描述符传递
- socket本地通信
正文

#define STDIN_FILENO 0
#define STDOUT_FILENO 1
#define STDERR_FILENO 2
一,管道进程的pipe函数和dup2函数组合使用父子进程间通信
参数是数组管道文件描述符
pipe参数是:
- fd[0]是读文件描述符,
- fd[2]是写文件描述符
int pipe(int pipefd[2]);
案例1:
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: pipe.c
> Author: songli
> QQ: 2734030745
> Mail: 15850774503@163.com
> CSDN: http://my.csdn.net/Poisx
> github: https://github.com/chensongpoixs
> Created Time: Fri 20 Oct 2017 10:22:29 PM CST
************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//管道数组文件描述符
int fd[2];
int ret;
int i, n = 2;
//创建管道
ret = pipe(fd);
//文件描述符
pid_t pid;
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("pipe error");
return -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
//创建子进程
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) // 异常处理
{
perror("fork error");
return -1;
}
else if (pid > 0) // 父进程的操作
{
printf("father fpid:%d, cpid:%d\n", getpid(), pid);
}
else if (pid == 0) //子进程的操作
{
printf("child fpid:%d, cpid:%d\n", getppid(), getpid());
break; //防止子线程创建子进程
}
}
//=============== 子进程的操作=============================
if (i == 0)
{
printf("no child n = %d, cpid:%d\n", i, getpid());
//=================写入数据 =====================
close(fd[0]); //关闭读取文件描述符
//标准输入也是 文件描述符 中的1
dup2(fd[1], STDOUT_FILENO);
// 执行 写入命令
execlp("ps", "ps", "-ef", NULL);
close(fd[1]); //关闭写入文件描述符
return 0; //signal 正常退出
}
if (i == 1)
{
printf("no child n = %d, cpid:%d\n", i, getpid());
//=================写入数据 =====================
close(fd[1]); //关闭 写描述符文件描述符
//标准输出也是 文件描述符 中的1
dup2(fd[0], STDIN_FILENO);
// 执行 写入命令
execlp("grep", "grep", "--color", "bash", NULL);
close(fd[0]); //关闭写入文件描述符
return 0; //signal 正常退出
}
//================= 主进程的操作 ========================
if (i == n)
{
//pcb 进程块pid
pid_t wpid;
int status;
while (1)
{
//等待线程
wpid = waitpid(-1, &status, WNOHANG );
if (wpid == 0) //有子进程程的操作
{
sleep(1);
continue;
}
else if (wpid == -1) // 没有子进程的操作
{
printf("退出子进程的wpid:%d\n", wpid);
exit(0);
}
else if (wpid > 0) //什么原因退出
{
if (WIFEXITED(status)) //正常退出
{
printf("子进程wpid:%d, status:%d\n", wpid, WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
if (WIFSIGNALED(status))
{
printf("子进程wpid:%d, status:%d\n", wpid, WTERMSIG(status));
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
效果图
1, 和fcntl函数一起使用可以数组read函数非阻塞
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: pipe_fcntl.c
> Author: songli
> QQ: 2734030745
> Mail: 15850774503@163.com
> CSDN: http://my.csdn.net/Poisx
> github: https://github.com/chensongpoixs
> Created Time: Fri 20 Oct 2017 10:47:08 PM CST
************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//数组文件描述符
int fd[2];
int ret;
char buf[1024];
//创建管道
ret = pipe(fd);
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("pipe error");
return -1;
}
//pcb进程控制块pid
pid_t pid;
//创建子线程
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) //异常处理
{
perror("fork error");
return -1;
}
else if (pid > 0) //父进程的处理
{
printf("father fpid:%d, cpid:%d\n", getpid(), pid);
//==============读取数据==================
close(fd[1]); //关闭写文件操作
//================== 在同一个进程中使用非阻塞使用fcntl函数 =========================================
int flags = fcntl(fd[0], F_GETFL );
flags |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(fd[0], F_SETFL, flags);
//=============================================================
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));
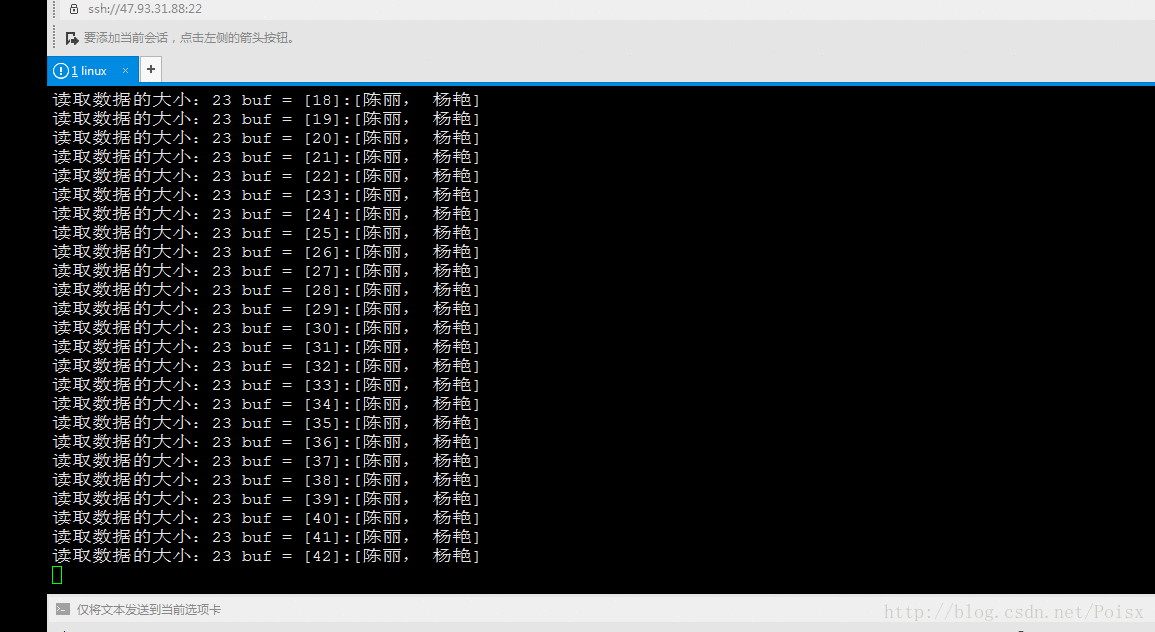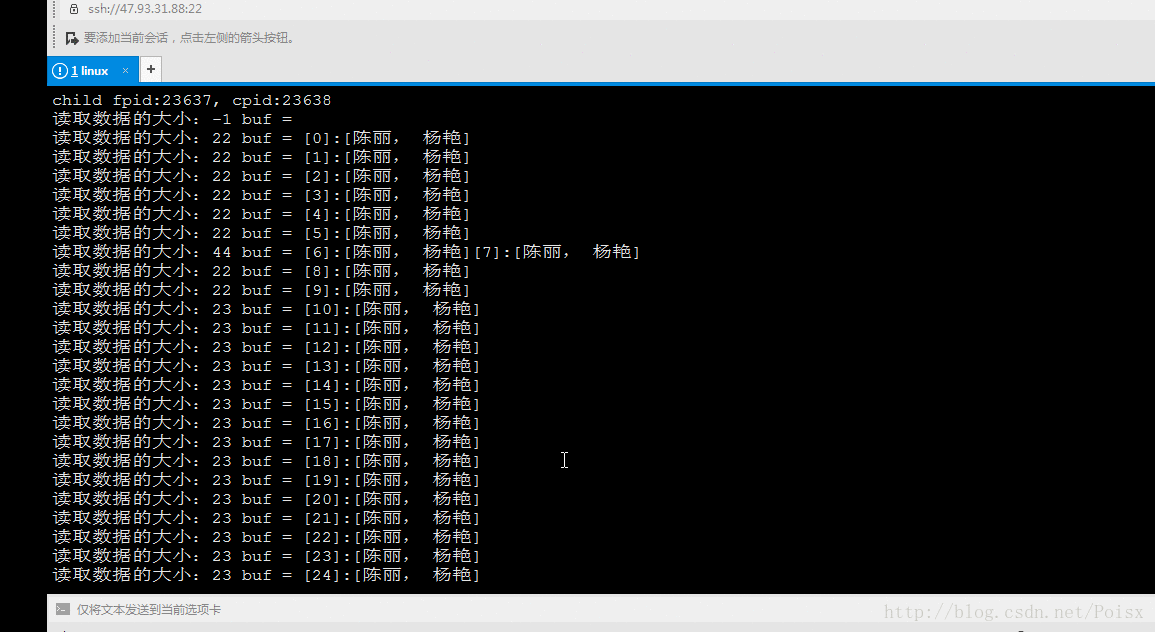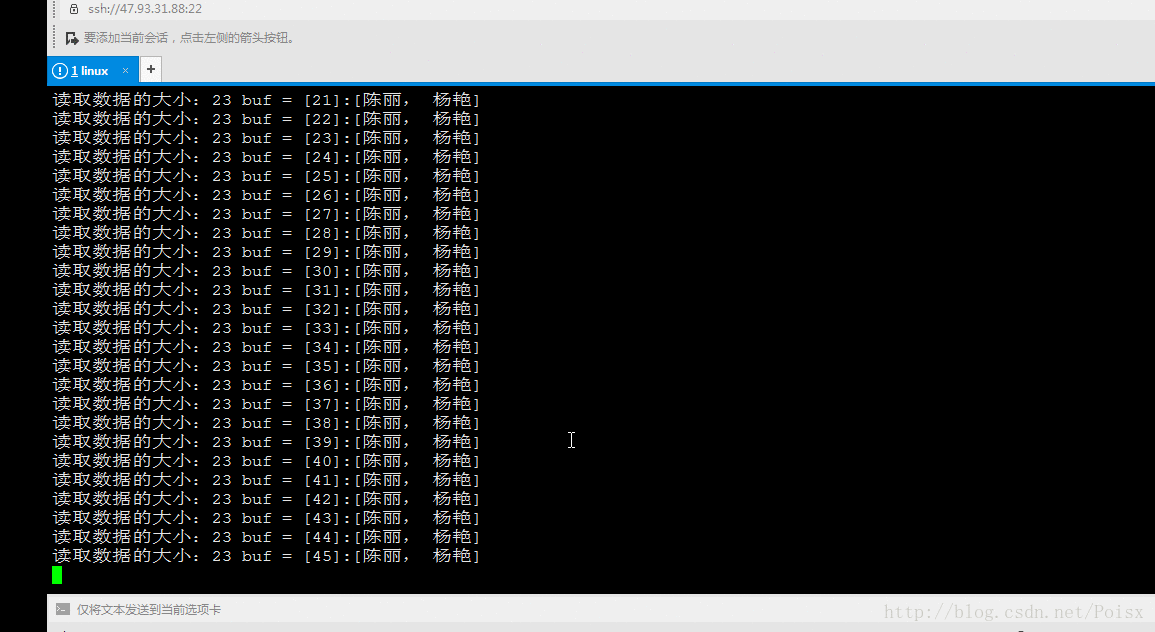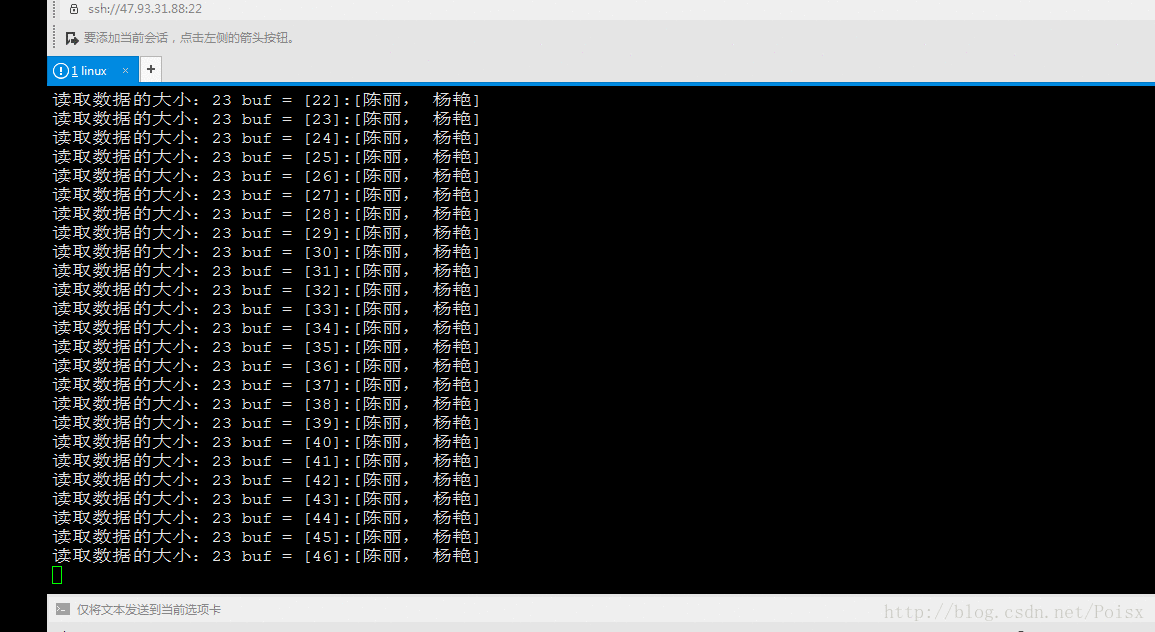
ret = read(fd[0], buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("读取数据的大小:%d buf = %s\n", ret, buf);
}
close(fd[0]);
}
else if (pid == 0) //子进程的操作
{
printf("child fpid:%d, cpid:%d\n", getppid(), getpid());
//========== 写操作===================
close(fd[0]); //关闭读取文件描述符
int i = 0;
while (1)
{
sleep(1);
memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));
sprintf(buf, "[%d]:[%s]", i++, "陈丽, 杨艳");
write(fd[1], buf, strlen(buf));
}
close(fd[1]);
}
return 0;
}
** 效果图**
二,管道 mkfifio函数的使用
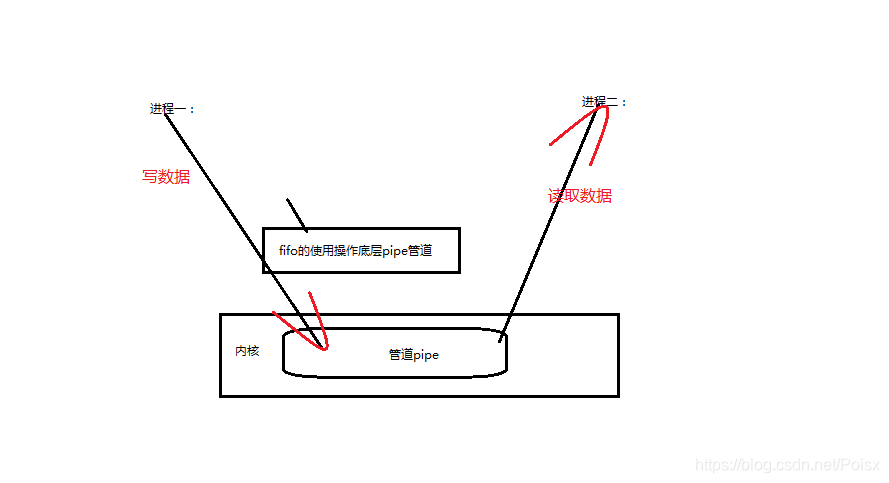
mkfifo命令生成管道文件

mkfifo函数 第一参数路径, 第二是权限
int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
1, 写入数据
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: fifo_write.c
> Author: songli
> QQ: 2734030745
> Mail: 15850774503@163.com
> CSDN: http://my.csdn.net/Poisx
> github: https://github.com/chensongpoixs
> Created Time: Fri 20 Oct 2017 11:22:50 PM CST
************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// 文件描述符
int fd;
int ret;
//判断是否创建管道文件
if ((ret = access("./myfifo", F_OK)) == -1)
{
//创建管道
ret = mkfifo("./myfifo", 0777);
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("mkfifo error");
return -1;
}
}
//打开文件
fd = open("./myfifo", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
//=====================写数据到管道中============================
while (1)
{
sleep(1);
write(fd, "陈丽, 杨艳", strlen("杨艳"));
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
2, 读取数据
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: fifo_read.c
> Author: songli
> QQ: 2734030745
> Mail: 15850774503@163.com
> CSDN: http://my.csdn.net/Poisx
> github: https://github.com/chensongpoixs
> Created Time: Fri 20 Oct 2017 11:31:07 PM CST
************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//文件描述符
int fd;
int ret;
char buf[1024];
//检测是否有管道文件
if ((ret = access("./myfifo", F_OK)) == -1)
{
ret = mkfifo("./myfifo", 0777);
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("mkfifo error");
return -1;
}
}
//打开管道文件
fd = open("./myfifo", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
//==============读取管道中数据=========================
while (1)
{
//================= 设置read函数非阻塞 ==================
/* int flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
flags |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags);*/
sleep(1);
memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));
ret = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("读取数据:%d, buf = %s\n", ret, buf);
}
//关闭文件
close(fd);
return 0;
}
效果图

三,mmap内存映射的机制
每个应用程序有虚的4个G的内存 由MMU把实际 要用的映射到内存中就是内核
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//文件描述符
int fd;
int len;
fd = open("./text.log", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
//文件大小
len = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END);
//参数一:NULL
//参数二:文件的大小,不能为0
//参数三:权限
//参数四:是否同步的硬盘中
//参数五:文件指针
//参数六:文件开始位置
void *ptr = mmap(NULL, len, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
if (ptr == MAP_FAILED)
{
perror("mmap error");
return -1;
}
char *p = (char*)ptr;
strcpy(p, "陈丽");
//参数一:文件指针
//参数二:文件大小
munmap(ptr, len);
//关闭文件
close(fd);
return 0;
}
1, 没有告关系的进程之间通信
写数据的
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//文件描述符
int fd;
int len; //文件大小
int ret; //状态码
//打开文件
fd = open("./text.log", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
//文件大小
len = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END);
//映射到内核中
void * ptr = mmap(NULL, len, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
if (ptr == MAP_FAILED)
{
perror("mmap error");
return -1;
}
char * p = (char *) ptr;
strcpy(p, "陈丽, 王蓉");
//关闭
munmap(ptr, len);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
读取数据
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
/**
读取数据mmap_read
**/
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//文件指针
int fd;
int len; //文件大小
void * ptr; //映射内存地址
char buf[1024];
//打开文件
fd = open("./text.log", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
//文件大小
len = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END);
//创建映射
ptr = mmap(NULL, len, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
if (ptr == MAP_FAILED)
{
perror("mmap error");
return -1;
}
//=============读取 map内存的数据===================
//while (1)
//{
//memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));
// read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
char *p = (char *) ptr;
printf("读取数据:%s\n", p);
//}
munmap(ptr, len);
//关闭文件操作
close(fd);
return 0;
}
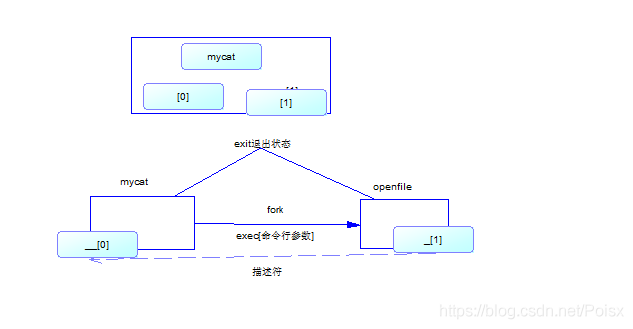
四, sockepair 父子进程通信
socketpair 是父子进程通信的一种:nginx使用master与worker进程之间的通信就是基于socketpair通信的
- 其实socketpair是基于pipe的通信的全双工的
- 父子进程之间的 “描述符传递”
- 流程- open, pipe,mkfifio, socket, accept
1, msghdr结构体
不幸,对于4.3BSD以及在其基础上构造的SunOS和Ultrix,以及从4.3BSD Reno开始的后续版本我们必须提供不同的实现。
为了交换文件描述符,调用sendmsg(2)和recvmsg(2)函数。这两个函数的参数中都
有一个指向msghdr的指针,该结构包含了所有关于要发送和接收消息的信息。该结
构定义在〈sys/socket.h〉 头文件中,在BSD4.3之下,其样式是:
strcut msghdr {
caddr_t msg_name; 可选的地址
int msg_namelen; 地址长度
struct iovec msg_iov; 散布/聚集数组
int msg_iovlen; 在msg_iov数组中的元素数
caddr_t msg_accrights; 存取权发送/接收到
int msg-accrightslen; 存取权缓存的长度
}
从4.3BSD Reno开始,更改了msghdr结构的定义。在以前版本中被称之为”存取权”
的最后两个元素改称为”辅助数据”。另外,在该结构结束处增加了一个新成员msg
_flags。
strcut msghdr {
caddr_t msg_name; 可选的地址
int msg_namelen; 地址长度
struct iovec msg_iov; 散布/聚集数组
int msg_iovlen; 在msg_iov数组中的元素数
caddr_t msg_control; 辅助数据
int msg-controllen; 辅助数据的长度
int msg_flags; 接收到消息的标志
}
我的内核查看
killer@localhost:~/socket$ uname -r
4.4.0-131-generic
实例程序
// gcc -o socketpair socketpair.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h> /* sockaddr_in{} and other Internet defns */
#include <arpa/inet.h> /* inet(3) functions */
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h> /* for nonblocking */
#include <sys/un.h> /* for Unix domain sockets */
#include <unistd.h> /* unlink */
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define BUFFSIZE 8192 /* buffer size for reads and writes */
/* define if struct msghdr contains the msg_control member */
#define HAVE_MSGHDR_MSG_CONTROL 1
ssize_t read_fd(int fd, void *ptr, size_t nbytes, int *recvfd)
{
struct msghdr msg;
struct iovec iov[1];
ssize_t n;
#ifdef HAVE_MSGHDR_MSG_CONTROL
union {
struct cmsghdr cm;
char control[CMSG_SPACE(sizeof(int))];
} control_un;
struct cmsghdr *cmptr;
msg.msg_control = control_un.control;
msg.msg_controllen = sizeof(control_un.control);
#else
int newfd;
msg.msg_accrights = (caddr_t) &newfd;
msg.msg_accrightslen = sizeof(int);
#endif
msg.msg_name = NULL;
msg.msg_namelen = 0;
iov[0].iov_base = ptr;
iov[0].iov_len = nbytes;
msg.msg_iov = iov;
msg.msg_iovlen = 1;
if ( (n = recvmsg(fd, &msg, 0)) <= 0)
return(n);
#ifdef HAVE_MSGHDR_MSG_CONTROL
if ( (cmptr = CMSG_FIRSTHDR(&msg)) != NULL &&
cmptr->cmsg_len == CMSG_LEN(sizeof(int))) {
if (cmptr->cmsg_level != SOL_SOCKET)
err_quit("control level != SOL_SOCKET");
if (cmptr->cmsg_type != SCM_RIGHTS)
err_quit("control type != SCM_RIGHTS");
*recvfd = *((int *) CMSG_DATA(cmptr));
} else
*recvfd = -1; /* descriptor was not passed */
#else
/* *INDENT-OFF* */
if (msg.msg_accrightslen == sizeof(int))
*recvfd = newfd;
else
*recvfd = -1; /* descriptor was not passed */
/* *INDENT-ON* */
#endif
return(n);
}
/* end read_fd */
ssize_t Read_fd(int fd, void *ptr, size_t nbytes, int *recvfd)
{
ssize_t n;
if ( (n = read_fd(fd, ptr, nbytes, recvfd)) < 0)
printf("read_fd error");
return(n);
}
int my_open(const char *pathname, int mode)
{
int fd, sockfd[2], status;
pid_t childpid;
char c, argsockfd[10], argmode[10];
socketpair(AF_LOCAL, SOCK_STREAM, 0, sockfd);
if ( (childpid = fork()) == 0) /* child process */
{
close(sockfd[0]);
snprintf(argsockfd, sizeof(argsockfd), "%d", sockfd[1]);
snprintf(argmode, sizeof(argmode), "%d", mode);
execl("./openfile", "openfile", argsockfd, pathname, argmode,
(char *) NULL);
printf("execl error");
}
/* parent process - wait for the child to terminate */
close(sockfd[1]); /* close the end we don't use */
waitpid(childpid, &status, 0);
if (WIFEXITED(status) == 0)
{
printf("child did not terminate");
}
if ( (status = WEXITSTATUS(status)) == 0)
{
Read_fd(sockfd[0], &c, 1, &fd);
}
else
{
errno = status; /* set errno value from child's status */
fd = -1;
}
close(sockfd[0]);
return(fd);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd, n;
char buff[BUFFSIZE];
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("usage: mycat <pathname>");
}
//O_RDONLY 只读取
if ( (fd = my_open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)) < 0)
{
printf("cannot open %s", argv[1]);
}
while ( (n = read(fd, buff, BUFFSIZE)) > 0)
{
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buff, n);
}
//exit(0);
return 0;
}

五 , socket本地通信
本地套接字使用 struct sockaddr_un ;的数据结构
bind的函数时候仍然需要强转
创建套接字需要使用 AF_UNIX ,AF_UNIX, AF_LOCAL
创建套接字的type可以选择TCP,也可以选择UDP,但是如果选择TCP,那么必须按照TCP的流程进行通信,如果选择UDP,必须按照UDP的流程进行通信。
1, client
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <netinet/udp.h>
#define SERV_NAME "sock.c"
#define SERV_NAMES "sock.s"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int listenfd;
struct sockaddr_un servaddr, cliaddr;
socklen_t len = sizeof(cliaddr);
char buf[256] = { 0 };
int ret, i = 0;
//创建socket
listenfd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
//绑定ip
unlink(SERV_NAME);
bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
servaddr.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(servaddr.sun_path, SERV_NAME);
if (bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)) < 0) {
perror("bind error");
return -1;
}
bzero(&cliaddr, sizeof(cliaddr));
servaddr.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(servaddr.sun_path, SERV_NAMES);
while (1) {
//发送数据
sprintf(buf, "陈丽 %d\n", i++);
sendto(listenfd, buf, strlen(buf), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
//接收数据
memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));
int ret = recvfrom(listenfd, buf, sizeof(buf), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&cliaddr, &len);
if (ret > 0) {
printf("client 接收消息:%s\n", buf);
}
sleep(1);
}
close(listenfd);
return 0;
}
2,server
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#define SERV_PORT 8888
#define SERV_NAME "sock.s"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int listenfd;
struct sockaddr_un servaddr, cliaddr;
socklen_t len = sizeof(cliaddr);
char buf[256] = { 0 };
int i, ret;
//创建socket
listenfd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
//绑定本地套接字
unlink(SERV_NAME); //删除绑定套接字
bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
servaddr.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(servaddr.sun_path, SERV_NAME);
if (bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)) < 0) {
perror("bind error");
return -1;
}
while (1) {
//接收数据
ret = recvfrom(listenfd, buf, sizeof(buf), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&cliaddr, &len);
if (ret > 0) {
printf("server :%s\n", cliaddr.sun_path);
sendto(listenfd, buf, strlen(buf), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&cliaddr, sizeof(cliaddr));
}
}
close(listenfd);
return 0;
}
六 , getsockname 函数
man 查看
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/socket.h>
int getsockname(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen);
DESCRIPTION
getsockname() returns the current address to which the socket sockfd is bound, in the buffer pointed to by addr. The addrlen argument should be ini‐
tialized to indicate the amount of space (in bytes) pointed to by addr. On return it contains the actual size of the socket address.
The returned address is truncated if the buffer provided is too small; in this case, addrlen will return a value greater than was supplied to the call.
RETURN VALUE
On success, zero is returned. On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.
ERRORS
EBADF The argument sockfd is not a valid descriptor.
EFAULT The addr argument points to memory not in a valid part of the process address space.
EINVAL addrlen is invalid (e.g., is negative).
ENOBUFS
Insufficient resources were available in the system to perform the operation.
ENOTSOCK
The file descriptor sockfd does not refer to a socket.
得到已经连接sockIP长度
//gcc -o getsocket getsocketname.c
//得到socket连接 IP地址长度
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h> /* sockaddr_in{} and other Internet defns */
#include <arpa/inet.h> /* inet(3) functions */
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h> /* for nonblocking */
#include <sys/un.h> /* for Unix domain sockets */
#include <unistd.h> /* unlink */
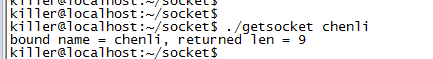
// cmd -> ./getsocket chenli
// screen -> bound name = chenli, returned len = 9
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int sockfd;
socklen_t len;
struct sockaddr_un addr1, addr2;
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("usage: unixbind <pathname>");
}
sockfd = socket(AF_LOCAL, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
unlink(argv[1]); /* OK if this fails */
bzero(&addr1, sizeof(addr1));
addr1.sun_family = AF_LOCAL;
strncpy(addr1.sun_path, argv[1], sizeof(addr1.sun_path)-1);
bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &addr1, SUN_LEN(&addr1));
len = sizeof(addr2);
getsockname(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &addr2, &len);
printf("bound name = %s, returned len = %d\n", addr2.sun_path, len);
//exit(0);
return 0;
}